December 2018 — A recent study by researchers from the University of New England and University of New Hampshire has demonstrated that flow imaging microscopy is an accurate, more efficient, and more informative method of elastin-like polymer (ELP) coacervate analysis than standard methods. ELP coacervates are a class of molecules with promising applications in drug delivery vehicles, tissue engineering, environmental remediation, and more. ELP coacervate architecture is stimuli-responsive and highly tunable, making them ideal for the above-mentioned applications.
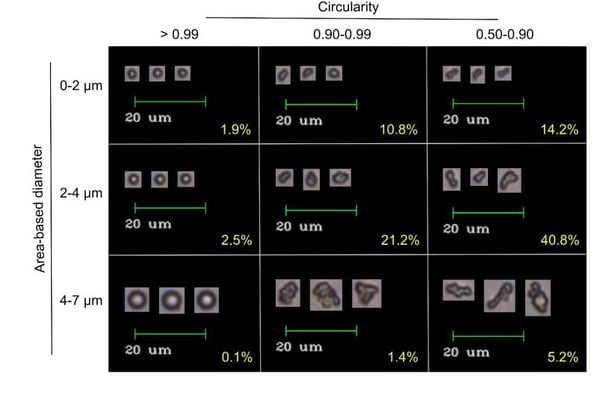
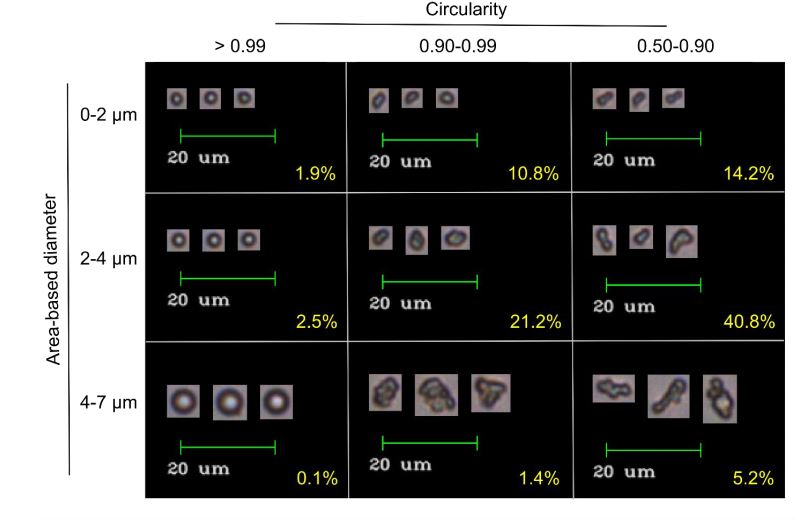
Pictured above: ELP coacervates imaged by the FlowCam. Size and circularity, two of the 40+ properties that can be measured by the FlowCam, is used to sort coacervates. Image from Marvin et al. (2018).
Standard methods for ELP coacervate analysis are indirect and cumbersome. Data from Visible-UV spectrophotometer turbidity measurements and dynamic light scattering (DLS) size measurements are superimposed to evaluate the formation of micron-scale aggregates, and particle geometry is constructed indirectly from diffusion data. Imaging analysis methods such as optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy are useful methods to acquire size and shape data, however it is time-consuming and laborious to acquire a large enough sample size to get statistically significant data.
In this study by the University of New England and University of New Hampshire, the size, morphology, and behavior of ELP coacervates subjected to various solvent conditions were measured and observed using the FlowCam particle analyzer. Results were validated by comparison with DLS and atomic force microscopy analyses. Flow imaging microscopy was demonstrated to be a successful method for ELP coacervate analysis. Additionally, flow imaging microscopy reported additional findings that were not measured using the DLS, microscopy, or Visible-UV spectrophotometry.
Access the full preprint, available on ChemRxiv, here.
Citation:
Marvin, L., Paiva, W., Gill, N., Morales, M.A., Halpern, J.M., Vesenka, J., Balog, E.R., 2018, Flow Imaging Microscopy as a Novel Tool for High-Throughput Evaluation of Elastin-like Polymer Coacervates. ChemRxiv. Preprint.