Visible particles are one of the most important sample attributes to monitor when developing and manufacturing biopharmaceuticals and other …
Read Post

Comprehensive characterization of biotherapeutics is often challenging, given their complexity. In many cases, singular analytical methods cannot …
Read Post
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are a type of nanocarrier with immense potential, serving as a tool to deliver nucleic acids like messenger RNA (mRNA) and …
Read Post
The risk of embolism, caused by particulate matter shed from medical device delivery systems, is a growing concern in the medical field. Ensuring …
Read Post

Pharmaceutical researchers face mounting pressure to track and control particles in their drug formulations throughout development. Strategies to …
Read Post

Subvisible particles (those 2-100 μm in diameter) in protein, cell, and gene therapies and other parenteral drug products pose risks to the safety …
Read Post
All biotherapeutics contain particulate matter, defined by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) as mobile undissolved particles that are …
Read Post
Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) have shown promise as vectors for gene therapy due to their non-pathogenic nature and effective infectivity for a …
Read Post
The protein aggregate content in protein therapies and other biological drug products is often a critical quality attribute that must be monitored. …
Read Post
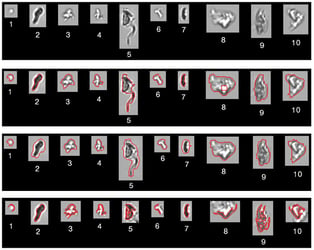
Scientists using FlowCam in biopharmaceutical research need to accurately assess many diverse particle types that may be present in their samples. …
Read Post

Protein aggregates in protein therapies can be difficult to monitor and measure in protein formulations due to their high transparency and irregular …
Read Post

Strategies for monitoring subvisible particles in biopharmaceutical formulations are central to developing and manufacturing safe, effective drug …
Read Post